Draw The Product Formed By The Reaction Of Tbutoxide
Draw The Product Formed By The Reaction Of Tbutoxide - As you can see, the reactant has stereospecificity, however, the product has none. Clearly show stereo the of the product. Chloride ion leaves in the process. Draw the correct stereoisomer of. The benzylic carbocation is stable because the positive charge is in resonance with the benzene ring. There are 2 steps to solve this one. For e2 reaction, the most substituted alkene is favored.
Chloride ion leaves in the process. When a strength of an acidic hydrogen and a leaving group is almost equal, then. (draw the correct stereoisomer of the product.) objective: Clearly show stereo the of the product.
As you can see, the reactant has stereospecificity, however, the product has none. Clearly show stereo the of the product. For e2 reaction, the most substituted alkene is favored. (draw the correct stereoisomer of the product.) objective: Draw the product formed by the reaction of t‑butoxide with (1r,2s)‑1‑bromo‑2‑methyl‑1‑phenylbutane (shown below). When a strength of an acidic hydrogen and a leaving group is almost equal, then.
Draw the major organic product formed when the compound shown below is
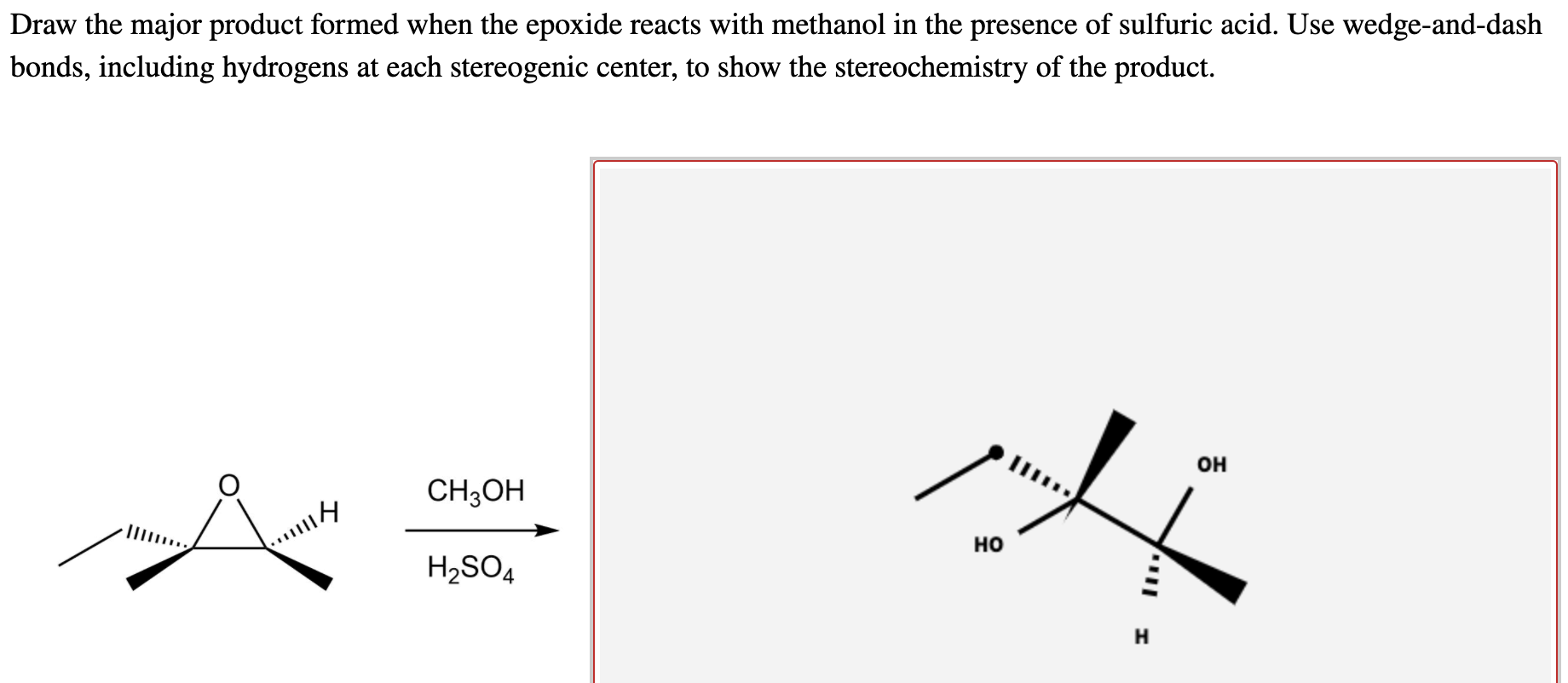
Solved Draw the major product formed when the epoxide reacts
Step 1/2first, let's identify the reactants in the reaction: When alkyl halide is treated with (ch a 3) a 3 co a − k a + elimination reaction occurs. Here’s the best way to solve it. Clearly show the stereochemistry of the product. Draw the product formed by the reaction of t‑butoxide with (1r,2s)‑1‑bromo‑2‑methyl‑1‑phenylbutane (shown below).
Br ch3 coh h3c h2 h3c. Here’s the best way to solve it. Step 1/2first, let's identify the reactants in the reaction: For e2 reaction, the most substituted alkene is favored.
The Reaction Is Typically Carried Out At.
For e2 reaction, the most substituted alkene is favored. Chloride ion leaves in the process. The benzylic carbocation is stable because the positive charge is in resonance with the benzene ring. Br ch3 coh h3c h2 h3c.
Draw The Correct Stereoisomer Of.
Clearly show stereo the of the product. Draw the product formed by the reaction of t‑butoxide with (1r,2s)‑1‑bromo‑2‑methyl‑1‑phenylbutane (shown below). As you can see, the reactant has stereospecificity, however, the product has none. Here’s the best way to solve it.
There Are 2 Steps To Solve This One.
When alkyl halide is treated with (ch a 3) a 3 co a − k a + elimination reaction occurs. (draw the correct stereoisomer of the product.) objective: Step 1/2first, let's identify the reactants in the reaction: Clearly show the stereochemistry of the product.
(Draw The Correct Stereoisomer Of The Product.)
When a strength of an acidic hydrogen and a leaving group is almost equal, then. (draw the correct stereoisomer of the product.) in regard to the.
As you can see, the reactant has stereospecificity, however, the product has none. Here’s the best way to solve it. When alkyl halide is treated with (ch a 3) a 3 co a − k a + elimination reaction occurs. (draw the correct stereoisomer of the product.) in regard to the. Clearly show the stereochemistry of the product.